Hash Table
Jun 2, 2025
What is Hash Table
A hash table is a data structure used to store key-value pairs. Each key is translated by hash function to a distinct index, also called hash code, within an array of buckets to get the desired value.
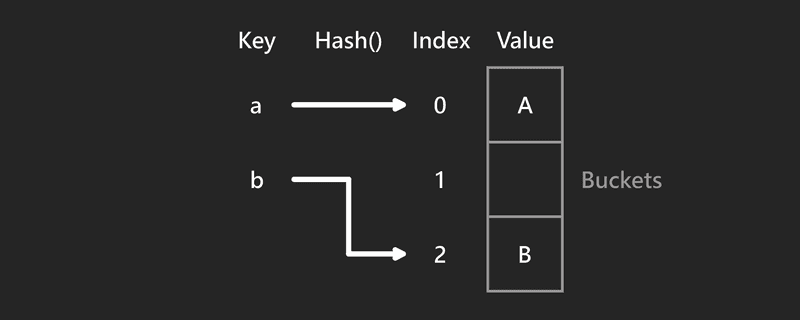 #
#Hash function
Hash functions are used to translate keys to array indexes, thus reducing collision and optimizing lookup speed, with a time complexity of O(1).
E.g., hashing by division hash(key) = key % table.size.
Collision resolution
Collisions occur when difference keys are mapped to the same index, requiring a method to distinguish between those keys map each to its own value.
E.g., linear probing rehash(index) = (index + 1) % table.size.
Load factor
The load factor, calculated as pairs.count / table.size, indicates how crowded
a table is. A high load factor may lead to longer search time and increased collisions.
It can be maintained through proper table resizing, also known as dynamic resizing.
Example
In many programming language, the hash table is implemented as basic data structure, often used for others such as sets and maps.
#Set
A set is a data structure using a hash table, containing pairs where the key and value are the same. Therefore, all values in it are distinct.
#s = set()s.add('a')# {'a'}s.add('b')# {'a', 'b'}s.add('a')# {'a', 'b'}python
Map
A map, also known as dictionary, is a data structure used to store key-value pairs.
#map = {'a': 'A', 'b': 'B'}map['c'] = 'C'# {'a': 'A', 'b': 'B', 'c': 'C'}value = map['a'] # 'A'python